Remote access may be permitted for privileged functions – Remote access to privileged functions offers organizations flexibility and efficiency, but it also introduces potential security risks. This comprehensive guide explores the risks and benefits of remote access, discusses security measures to mitigate these risks, and provides best practices for managing remote access to privileged functions.
The following sections will delve into authentication and authorization methods, access control models, monitoring and logging techniques, incident response strategies, and essential best practices for ensuring the security of privileged functions accessed remotely.
Remote Access Privileges: Remote Access May Be Permitted For Privileged Functions

Remote access to privileged functions allows authorized users to access and control critical systems and data remotely. While this can provide convenience and flexibility, it also introduces potential security risks.
Benefits of allowing remote access to privileged functions include:
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Improved collaboration and teamwork
- Reduced downtime and increased system availability
Risks associated with allowing remote access to privileged functions include:
- Increased exposure to unauthorized access and attacks
- Potential for data breaches and system compromise
- Difficulty in monitoring and controlling remote access
To mitigate these risks, it is essential to implement robust security measures, such as:
- Strong authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Least privilege principle
- Regular security audits and monitoring
- Incident response plans
Authentication and Authorization
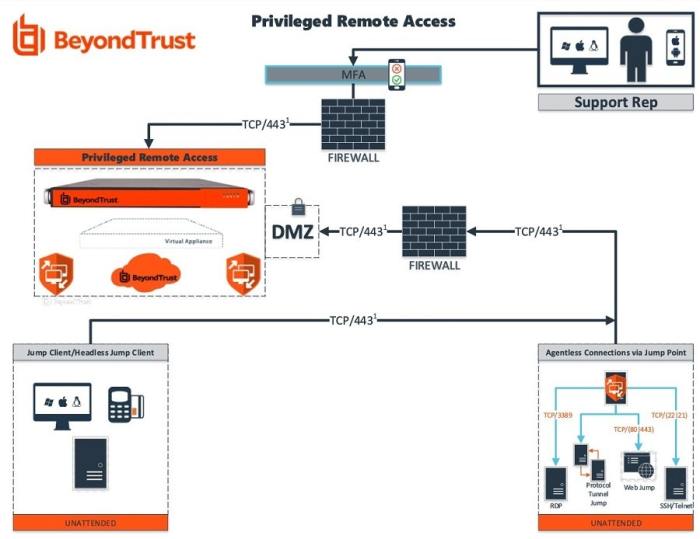
Authentication and authorization are critical components of controlling access to privileged functions remotely. Authentication verifies the identity of the user, while authorization determines the level of access that the user has.
Common authentication methods include:
- Username and password
- Biometrics (e.g., fingerprint, facial recognition)
- Two-factor authentication (2FA)
- Smart cards
Common authorization methods include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
- Rule-based access control (RBAC)
For example, in a healthcare organization, a doctor may have access to patient records based on their role, while a nurse may have access to a more limited set of records.
Access Control
Access control models define the rules and mechanisms for managing access to privileged functions remotely.
Common access control models include:
- Discretionary access control (DAC)
- Mandatory access control (MAC)
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
DAC allows users to control access to their own resources, while MAC enforces access restrictions based on security labels. RBAC and ABAC are more flexible models that allow for fine-grained access control based on roles or attributes.
Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging are essential for detecting and investigating security incidents involving remote access to privileged functions.
Information that should be logged includes:
- User activity (e.g., logins, commands executed)
- System events (e.g., file changes, network connections)
- Security alerts (e.g., failed login attempts, malware detections)
Regularly reviewing logs and monitoring for suspicious activity can help identify and mitigate security risks.
Incident Response

In the event of a security incident involving remote access to privileged functions, it is important to follow a well-defined incident response plan.
Steps to take in the event of an incident include:
- Contain the incident to prevent further damage
- Identify the root cause of the incident
- Remediate the vulnerability
- Recover from the incident
- Learn from the incident to prevent future occurrences
Best practices for incident response include:
- Having a dedicated incident response team
- Using automated tools to detect and respond to incidents
- Regularly testing incident response plans
Best Practices
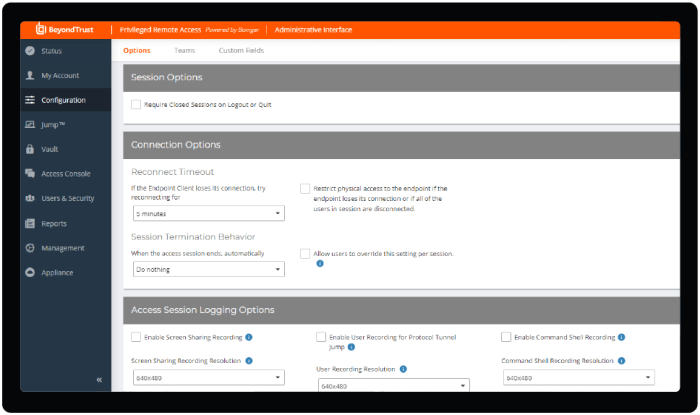
To reduce the risk of security breaches, it is essential to follow best practices for managing remote access to privileged functions.
Best practices include:
- Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Implement the least privilege principle
- Monitor and log remote access activity
- Have an incident response plan in place
- Regularly audit and review security controls
By following these best practices, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access to privileged functions and protect their critical systems and data.
Questions and Answers
What are the primary risks associated with remote access to privileged functions?
Remote access introduces the risk of unauthorized access to critical systems and data, potential malware infections, and increased exposure to cyberattacks.
How can organizations mitigate the risks of remote access?
Implementing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, enforcing access control policies, monitoring and logging remote access activities, and establishing incident response plans are essential for mitigating risks.
What are the best practices for managing remote access to privileged functions?
Best practices include using multi-factor authentication, implementing least privilege principles, regularly reviewing and updating access permissions, monitoring and logging all remote access activities, and conducting regular security audits.