Embark on an exploration of prokaryotic cells vs eukaryotic cells worksheet, a resource that delves into the fundamental differences between these two cell types, providing a comprehensive overview of their structure, function, and evolutionary significance.
This worksheet is designed to guide you through the intricacies of cell biology, equipping you with a deep understanding of the building blocks of life.
Overview of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
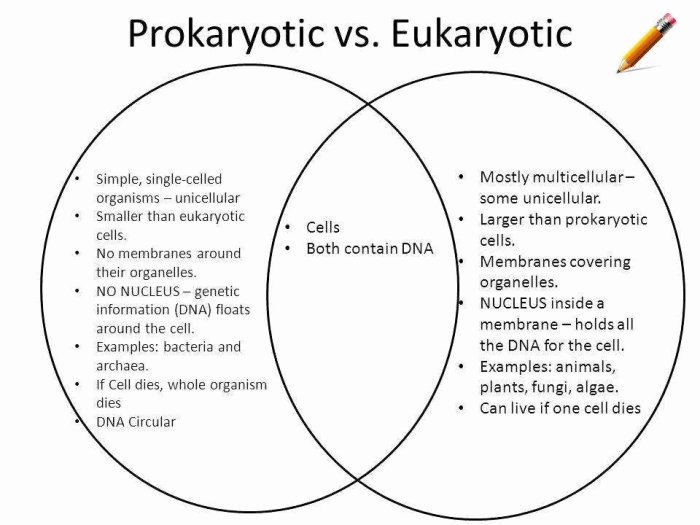
Cells, the fundamental units of life, exhibit two distinct types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, simpler and more ancient, lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, eukaryotic cells, more complex and evolved, possess a nucleus and an array of specialized organelles.
The table below Artikels the key characteristics that differentiate prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Typically 0.1-5 µm | Typically 10-100 µm |
| Shape | Diverse, including spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral | Variable, often determined by cell function |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present, surrounded by a nuclear membrane |
| Membrane-bound Organelles | Absent | Present, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 80S |
| Cell Division | Binary fission | Mitosis or meiosis |
Structure and Function of Prokaryotic Cells

Prokaryotic cells, the simpler of the two cell types, exhibit a basic structure that enables their survival in diverse environments.
The cell membrane, a phospholipid bilayer, serves as a protective barrier and regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
The cytoplasm, a gel-like substance, contains ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis, and a single, circular chromosome that carries the cell’s genetic material.
Other structures, such as pili and flagella, may be present to facilitate attachment to surfaces or movement.
Structure and Function of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells, more complex than prokaryotic cells, exhibit a remarkable level of organization and specialization.
The nucleus, enclosed by a double membrane, houses the cell’s genetic material, organized into multiple linear chromosomes.
The endoplasmic reticulum, a network of membranes, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification.
The Golgi apparatus, a series of flattened sacs, modifies and packages proteins and lipids for secretion.
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, generate energy through cellular respiration.
Other organelles, such as lysosomes and vacuoles, contribute to digestion and waste removal.
Similarities and Differences in Cell Division: Prokaryotic Cells Vs Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
Cell division, essential for growth and reproduction, occurs differently in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission, a simple process where the cell replicates its DNA and divides into two identical daughter cells.
Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis, a more complex process that involves the formation of mitotic spindles and the separation of chromosomes into two sets, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Meiosis, a specialized form of cell division, occurs in eukaryotic cells to produce gametes (sex cells) with half the number of chromosomes.
Evolutionary Significance of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells

Prokaryotic cells, the first cells to evolve, have persisted for billions of years, adapting to diverse environments.
The evolution of eukaryotic cells, with their greater complexity and specialization, allowed for the development of multicellular organisms and increased biological diversity.
The endosymbiotic theory suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts, essential organelles in eukaryotic cells, originated as free-living prokaryotic cells that were engulfed by a larger cell and formed a symbiotic relationship.
Helpful Answers
What are the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess a true nucleus and a variety of membrane-bound organelles.
How do prokaryotic cells divide?
Prokaryotic cells divide through binary fission, a simple process that results in two identical daughter cells.
What is the function of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material and plays a central role in regulating cell activities.